News
The Importance of Equol (2)
2024-07-15 14:16:51
Hits:0
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), now known as metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatopathy (MASLD) is defined as the accumulation of excess fat in the form of triglycerides in the liver (steatosis) (>5% of the hepatocyte tissue). Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease may worsen and lead to liver inflammation (enlargement or swelling) and damage called nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH, renamed MASH),and cirrhosis (scarring buildup) may occur if NASH progresses.
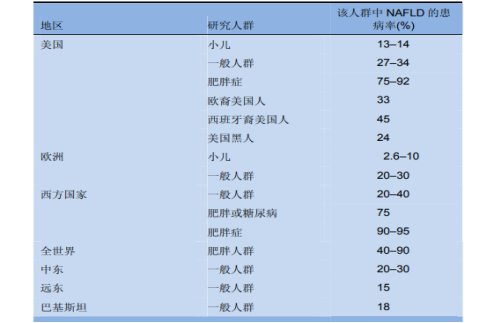
Liver disease is a major global public health problem.On May 21, 2010 the 63rd World Health Organization World Assembly adopted a resolution to designate July 28 as World Hepatitis Day. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is becoming more common as the number of people with obesity increases, especially in the Middle East and Western countries , and the prevalence of NAFLD has doubled in the last two decades. The prevalence of NAFLD is much higher in postmenopausal women than in premenopausal women, which is attributed to the decreased estrogen levels in postmenopausal women. Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and its downstream signaling pathway are inhibited by the estrogen signaling pathway, thus estrogen deficiency increases the level of inflammatory factors in the body. Hormone replacement therapy, while improving liver inflammation and steatosis in postmenopausal NAFLD, may increase the risk of breast cancer.[4].
Equol is one of the soy isoflavones and its metabolites with the highest estrogen-likeactivity and antioxidant activity. It has shown promising results in alleviating female menopausal symptoms, as well as preventing cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, chronic kidney disease, and malignant tumors. In order to investigate the effects and possible mechanisms of action of Equol intervention on postmenopausal NAFLD, the researchers established a postmenopausal NAFLD model by feeding de-ovulated rats with high-fat diet (HFD) for observation. After 60 5-week-old female SD rats were sham-operated or ovariectomized (OVX), 10 sham-operated rats were taken as the sham-operated group and fed with normal chow; the other 50 OVX rats were divided into the OVX+HFD group according to the method of randomized numerical table. It was found that Equol could effectively improve NAFLD induced by high-fat diet and de-ovulated rats, which was manifested by the maintenance of higher levels of serum estrogens after Equol intervention, the reduction of body mass, hepatic index, HOMA-IR, inflammation level and hepatic steatosis in OVX+HFD rats, the improvement of liver function and lipid metabolism disorders in the rats, and the down-regulation of hepatic TNF-α and IL-6 mitochondria, as well as the down-regulation of hepatic TNF-α and IL-6 matochondria. α and IL-6 mRNA and NF-κB p-p65 protein levels in liver tissues, and the effects of estramustine were more pronounced with the increase of the intervention dose[4]. This study provides a new scientific basis for revealing the clinical prevention and treatment of NAFLD in postmenopausal women with Equol.
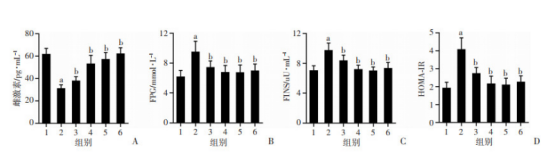
各组大鼠雌激素、FPG、FINS水平及HOMA-IR比较(图1)
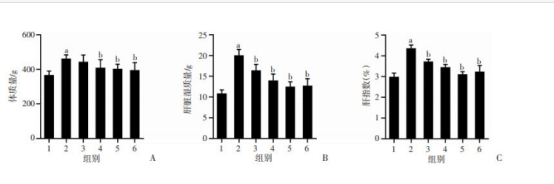
各组大鼠体质量、肝脏湿质量、肝指数比较(图2)
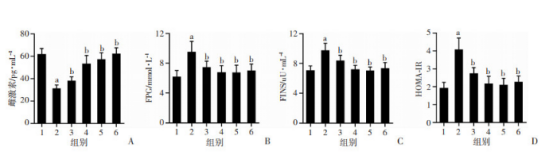
各组大鼠雌激素、FPG、FINS水平及HOMA-IR比较(图3)
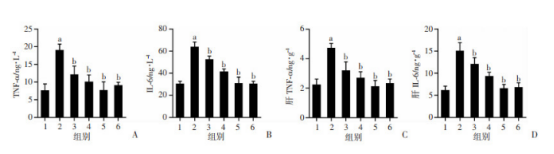
各组大鼠雌激素、FPG、FINS水平及HOMA-IR比较(图4)
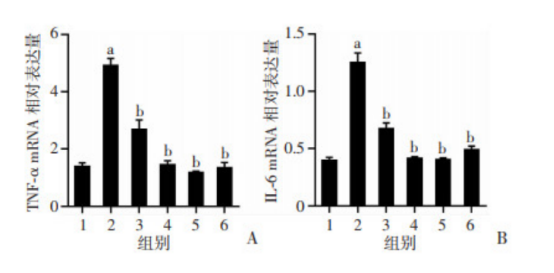
各组大鼠肝组织炎症因子mRNA表达水平比较(图5)
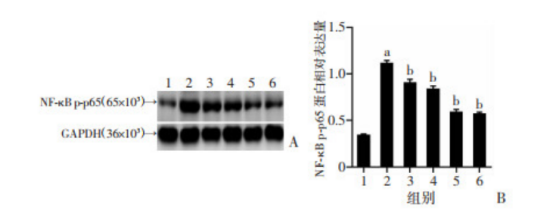
各组大鼠肝组织NF-κB p-p65蛋白表达水平比较(图6)
参考:
[1]https://liverfoundation.org/zh-CN/%E8%82%9D%E8%84%8F%E7%96%BE%E7%97%85/%E8%84%82%E8%82%AA%E8%82%9D%E7%96%BE%E7%97%85/%E9%9D%9E%E9%85%92%E7%B2%BE%E6%80%A7%E8%84%82%E8%82%AA%E8%82%9D/
[2]《世界胃肠病学组织全球指南--非酒精性脂肪性肝病及非酒精性脂肪性肝炎》浙江大学医学院附属邵逸夫医院消化科(310016)陈小丽 译 戴宁 审校, 2012 年 6 月
[3]https://www.mayoclinic.org/zh-hans/diseases-conditions/nonalcoholic-fatty-liver-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20354567?sscid=51k8_pkl7l&
[4]ZHANG Guiming, NI Xiangmin, CUI Hanqiang, XU Zhe, LI Shuo, WANG Jian. Effect of equol intervention on high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in ovariectomized rats[J]. Journal of Army Medical University, 2022, 44(21): 2129-2137. DOI: 10.16016/j.2097-0927.202204122