News
Importance of Nervonic Acid
2024-06-13 14:33:20
Hits:0
Multiple sclerosis (hencefore MS) is the most common central nerve demyelinating disease in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This damage disrupts the ability of parts of the nervous system to transmit signals, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. Specific symptoms can include double vision, vision loss, eye pain, muscle weakness, and loss of sensation or coordination.[1]
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is an animal model widely used for mechanistic and translational study of MS.[2]
The study utilized C57BL/6 mice and divided them into six groups: model group, control group, drug treatment group, and three different doses of nervonic acid groups, aiming to investigate the effects of nervonic acid on inflammation and its potential mechanisms in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). The impacts of nervonic acid on spinal cord inflammation infiltration and demyelination in mice were observed through hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Luxol Fast Blue (LFB) myelin staining. The results demonstrated that nervonic acid treatment significantly inhibited the development and severity of EAE in mice (Fig.1), reduced inflammation in the spinal cord of mice related to autoimmunity (Fig.2), alleviated inflammation infiltration and demyelination in the spinal cord of mice (Fig.3), and increased the expression of antioxidant proteins and anti-inflammatory cytokines (Fig.4). Therefore, nervonic acid might be a strong candidate for intervening in multiple sclerosis and other autoimmune diseases, offering a new potential therapeutic option for the treatment of multiple sclerosis.
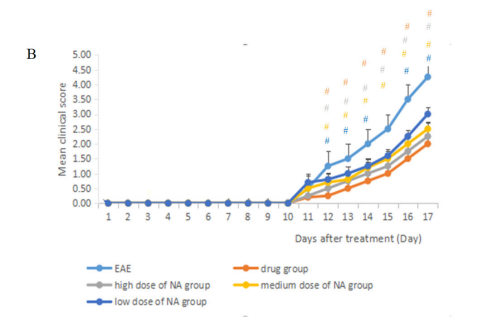
不同组小鼠的临床症状的发展和严重程度监测 图1
The development and severity of clinical signs in the
different groups of mice were monitored in Fig. 1
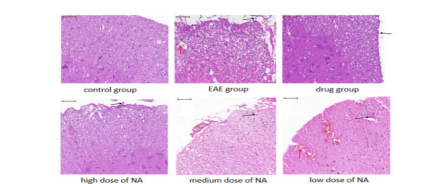
NA 治疗可减轻小鼠脊髓中与自身免疫相关的炎症 图2
Treatment with NA mitigated autoimmunity-related inflammation in the spinal cords of mice in Fig.2
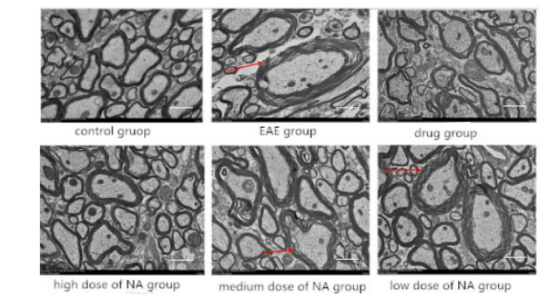
NA 治疗可减轻小鼠脊髓脱髓鞘 图3
Treatment with NA mitigated demyelination in the spinal cords of mice in Fig.3
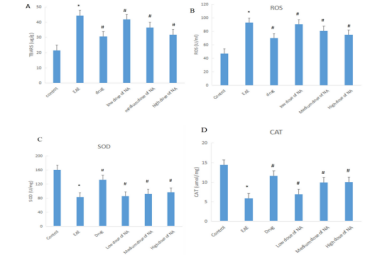
神经酸抑制EAE氧化应激状态(图4)
NA treatment inhibited the oxidative stress status of EAE in Fig.4
References:[1]National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. 2015-11-19 [2016-03-06].
[2] Act1介导的IL-17信号通路与自身免疫性脑脊髓炎关系的研究进展 《生命科学》 2017, 29(9): 891-897
[3] Aihaiti M, Shi H, Liu Y, Hou C, Song X, Li M, Li J. Nervonic acid reduces the cognitive and neurological disturbances induced by combined doses of D-galactose/AlCl3 in mice. Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Jul 6;11(10):5989-5998. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3533. PMID: 37823115; PMCID: PMC10563680.
[4] Engber, Daniel. The Trouble With Black-6: A tiny alcoholic takes over the lab.. Slate.com. 17 November 2011 [2021-12-29].
[5] https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E8%8B%8F%E6%9C%A8%E7%B2%BE-%E4%BC%8A%E7%BA%A2%E6%9F%93%E8%89%B2