News
The Significance of Nervonic Acid (2)
2024-03-19 14:53:18
Hits:0
Adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) is an X-linked inherited peroxisomal disorder due to mutations in the ALD protein (ALDP) and characterized by accumulation of very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFA), specifcally hexacosanoic acid (C26:0) particularly in plasma, brain white matter, and the adrenal cortex.[2]
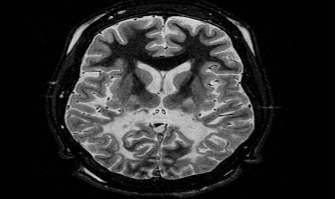
MRI demonstrates loss of posterior white matter
sources:Radiopedia
Using ALD patient-derived fbroblasts the study examined whether nervonic acid can reverse VLCFA accumulation similar to erucic acid.It has shown that nervonic acid can reverse total lipid C26:0 accumulation in a concentration-dependent manner in ALD cell lines( Fig.1). Further,it shows that nervonic acid can protect ALD fbroblasts from oxidative insults, presumably by increasing intracellular ATP production.(Fig.2) Thus, nervonic acid can be a potential therapeutic for individuals with ALD, which can alter cellular biochemistry and improve its function.[2]
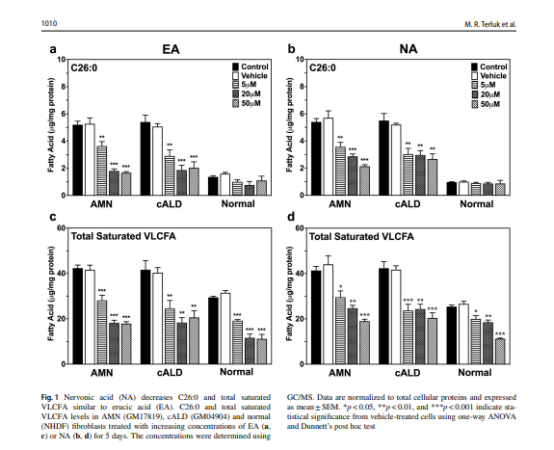
Nervonic acid showed a consistent concentration-dependent decrease in VLCFA, especially in the AMN cell line (Fig. 1).
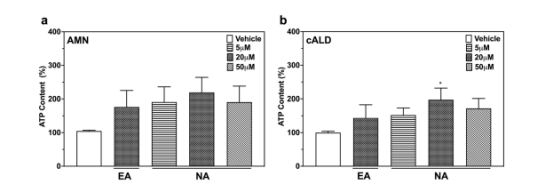
Effect of nervonic acid (NA) on ATP production in ALD fibroblasts(Fig.2)
参考:[1]McGuinness MC, Lu JF, Zhang HP, Dong GX, Heinzer AK, Watkins PA, et al. Role of ALDP (ABCD1) and mitochondria in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23(2):744–53
[2] Terluk, Marcia R et al. “Nervonic Acid Attenuates Accumulation of Very Long-Chain Fatty Acids and is a Potential Therapy for Adrenoleukodystrophy.” Neurotherapeutics : the journal of the American Society for Experimental NeuroTherapeutics vol. 19,3 (2022): 1007-1017. doi:10.1007/s13311-022-01226-7