News
The Significance of Nervonic Acid
2024-03-12 15:23:44
Hits:0
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a chronic neurodegenerative disorder that affects the central nervous system, primarily impacting the motor system. As the second most severe health issue among neurodegenerative diseases, PD affects about 3% of the population over 60 years old. The symptoms of Parkinson's typically develop slowly over time, with the most noticeable early symptoms being tremors, limb rigidity, decreased motor function, and abnormal gait. Nervonic acid can dose-dependently alleviate behavioral deficits induced by MPTP. Moreover, nervonic acid does not have toxic effects on the liver and kidneys of mice. Notably, research has found that nervonic acid significantly ameliorated the impact of MPTP damage on striatal dopamine, serotonin, and their metabolites. In addition, tyrosine hydroxylase was upregulated, α-synuclein was downregulated, and oxidative stress was partly inhibited after treatment with nervonic acid, as indicated by the upregulation of superoxide dismutase and glutathione activity. These research findings reveal the potential of nervonic acid to protect the motor system from motor disorders in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease (PD) without any side effects, indicating that nervonic acid could be an alternative strategy for alleviating symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
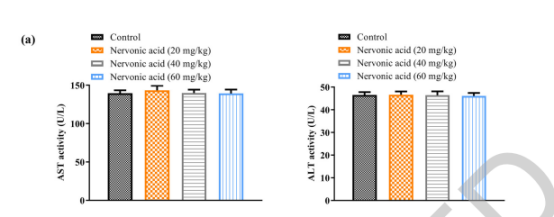
(神经酸对小鼠的肝脏和肾脏没有毒性影响)
NA displayed no toxicity on mouse liver and kidney.
Alzheimer's disease (AD), commonly known as senile dementia or old age dementia, is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by a slow onset and progressively worsening over time. The most common early symptom is the loss of short-term memory (difficulty in remembering recent events). As the disease progresses, symptoms that may gradually emerge include language impairments, disorientation (including getting lost easily), mood swings, loss of motivation, inability to take care of oneself, and many behavioral issues. Nervonic acid (NA) is an ultra-long-chain monounsaturated fatty acid that can repair nerve cell damage caused by oxidative stress. Research has established an AD mouse model using a combined dosage of D-galactose/AlCl3 and treated it with different doses of NA (10.95 and 43.93 mg/kg). The results showed that nervonic acid delayed the decline in motor and learning abilities caused by D-galactose/AlCl3, increased the activity of total superoxide dismutase, peroxidase, and glutathione peroxidase in the body, and reduced the content of malondialdehyde. Additionally, nervonic acid reduced the levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), aspartate aminotransferase, and alanine aminotransferase in the hippocampus and liver tissues caused by D-galactose/AlCl3, increased the levels of serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid, and alleviated the morphological damage to cells. Moreover, the intervention with nervonic acid upregulated the expression levels of the PI3K, AKT, and mTOR genes and downregulated the expression levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β genes. Therefore, the study speculates that the intervention with nervonic acid may effectively improve cognitive impairment by activating the PI3K signaling pathway. These results indicate that nervonic acid has potential as an antioxidant drug for the prevention and early treatment of Alzheimer's disease.

NA对D-半乳糖/AlCl3诱导小鼠相关抗氧化指标的影响
Effect of NA on related antioxidant indices in D-galactose/AlCl3-induced mice
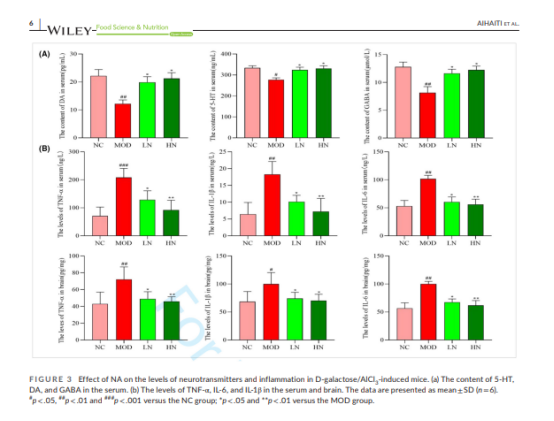
NA 对 D-半乳糖/AlCl3 诱导小鼠神经递质水平和炎症的影响。 (a)血清中5-HT、DA、GABA的含量。 (b)血清和脑中TNF-α、IL-6和IL-1β的水平。
Effect of NA on the levels of neurotransmitters and inflammation in D-galactose/AlCl3-induced mice. (a) The content of 5-HT, DA, and GABA in the serum. (b) The levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in the serum and brain.
References:(1)Politis M. Neuroimaging in Parkinson disease: from research setting to clinical practice. Nat Rev Neurol. 2014 Dec;10(12):708–22.
(2) Parkinson's Disease Information Page. NINDS. 2016-06-30 [2016-07-18].
(3) Hu, Dandong, Cui, Yujuan and Zhang, Ji. "Nervonic acid amends motor disorder in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease" Translational Neuroscience, vol. 12, no. 1, 2021, pp. 237-246. https://doi.org/10.1515/tnsci-2020-0171
(4)Steve; Burns, Alistair. Alzheimer’s disease. BMJ. 2009-02-05, 338: b158 [2019-01-01]. ISSN 1468-5833. PMID 19196745. doi:10.1136/bmj.b158.
(5)Aihaiti, Mayile et al. “Nervonic acid reduces the cognitive and neurological disturbances induced by combined doses of D-galactose/AlCl3 in mice.” Food science & nutrition vol. 11,10 5989-5998. 6 Jul. 2023, doi:10.1002/fsn3.3533